类:
降低维护成本、使代码高度复用、扩充方便灵活
OOP 面向对象开发
核心:封装
类->工厂->对象
ES6中的类
//车类 class Car{ 构造函数 constructor(){ console.log("开始造车"); } } 实例化,类->对象 let c=new Car();
构造函数的写法有点类似于简洁表示法:
构造函数的写法类似简洁表示法 let obj={ 普通写法 fn:function(){ },简洁表示法 fn2(){ } }
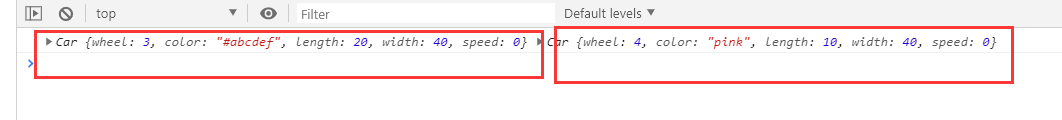
构造函数 constructor(wheel,color,length,width){接收参数 给属性赋值,this指向当前实例化的结果 this.wheel=wheel; this.color=color; this.length=length; this.width=width; this.speed=0; } 方法 speedUp(){ this.speed+=1; } } new Car(3,"#abcdef",20,40); console.log(c); c.speedUp();调用实例(对象)的方法 console.log(c.speed);获取实例(对象)的属性

不同实例之间是相互独立的
实例化,类->对象 let c1=); let c2=new Car(4,"pink",10,1)">); console.log(c1,c2);
音乐播放器类实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<Meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>ES6 class</title>
</head>
<style>
</style>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<script>
模拟一个播放器类
class AudioPlayer{
constructor(container){this.container=document.querySelector(container);
this.songsList=[];
this.dom=null;
this.audio=new Audio();
this.status=0;标记播放器的状态
this.getSongs();获取歌单列表
this.createElement();创建DOM
this.bindEvent();绑定事件
this.render();渲染到页面
}
getSongs(){
模拟ajax请求拿数据
[
{
songName:"name1",songCover:"cover1",封面
songSinger:"singer1",1)">歌手
songUrl:"url1"资源地址
},{
songName:"name2"封面
songSinger:"singer2",1)">歌手
songUrl:"url2" }
];
}
createElement(){
const div=document.createElement("div");
div.innerHTML=`
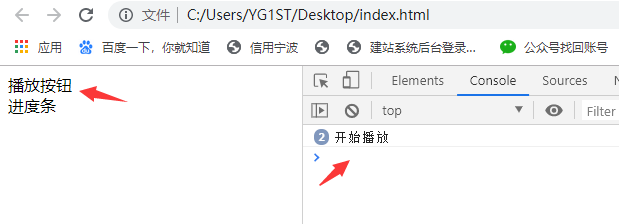
<div class="btn">播放按钮</div>
<div>进度条</div>
`;
div;
}
bindEvent(){
this.dom.querySelector(".btn").addEventListener("click",()=>{
console.log("开始播放");
})
}
render(){
this.container.appendChild(this.dom);
}
}
new AudioPlayer("#app");
</script>
</body>
</html>